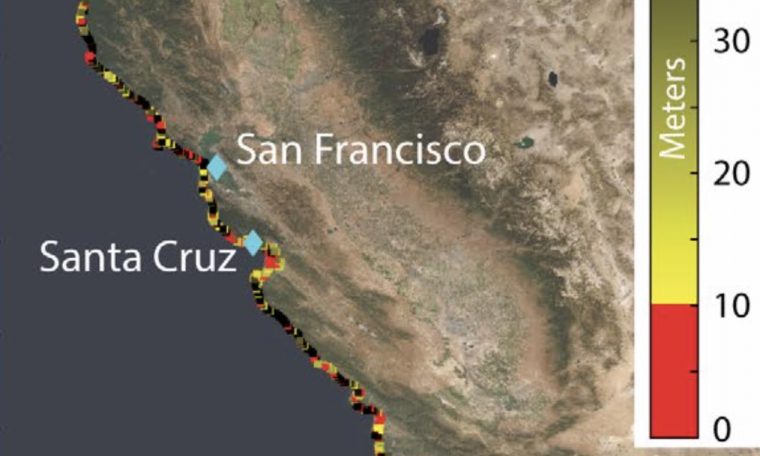
Coastal elevation in California. Coastal zones, which are outlined to be these with elevations fewer than 10 m, are shown in red. Segments of the coastline with elevations larger than 10 m are colored by a yellow gradient. Credit: USGS NED
A vast majority of the world populace lives on low lying lands close to the sea, some of which are predicted to submerge by the stop of the 21st century because of to mounting sea concentrations.
The most pertinent amount for examining the impacts of sea-degree alter on these communities is the relative sea-amount increase — the elevation improve involving the Earth’s floor top and sea surface area peak. For an observer standing on the coastland, relative sea-stage rise is the net change in the sea degree, which also consists of the increase and tumble of the land beneath observer’s toes.
Now, utilizing exact measurements from condition-of-the-artwork satellite-based interferometric artificial aperture radar (InSAR) that can detect the land surface area increase and fall with millimeter accuracy, an Arizona Condition College analysis workforce has, for the 1st time, tracked the entire California coast’s vertical land movement.
They’ve discovered area hotspots of the sinking coastline, in the cities of San Diego, Los Angeles, Santa Cruz, and San Francisco, with a blended population of 4 to 8 million individuals exposed to quick land subsidence, who will be at a increased flooding risk in the course of the a long time forward of projected sea-level rise.
“We have ushered in a new period of coastal mapping at better than 1,000 fold higher depth and resolution than ever ahead of,” stated Manoochehr Shirzaei, who is the principal investigator of the NASA-funded job. “The unprecedented detail and submillimeter precision resolved in our vertical land motion dataset can change the comprehending of natural and anthropogenic changes in relative sea-degree and associated hazards.”
The results have been released in this week’s challenge of Science Improvements.
The investigation staff bundled graduate university student and guide author Em Blackwell, and college Manoochehr Shirzaei, Chandrakanta Ojha, and Susanna Werth, all from the ASU College of Earth and Place Exploration (Werth has a dual appointment in the University of Geography and City Preparing).
Em Blackwell experienced a keen desire in geology, and as Blackwell began graduate college, the purposes of InSAR drew them to go after this undertaking. InSAR uses radar to measure the adjust in distance among the satellite and ground floor, developing very correct deformation maps of the Earth’s floor at 10s m resolution over 100s km spatial extent.
Land subsidence can come about because of to normal and anthropogenic procedures or a mix of them. The natural procedures comprise tectonics, glacial isostatic adjustment, sediment loading, and soil compaction. The anthropogenic leads to include things like groundwater extraction and oil and gasoline manufacturing.
As of 2005, roughly 40 million people today were exposed to a 1 in 100-12 months coastal flooding hazard, and by 2070 this variety will grow a lot more than threefold. The price of home exposed to flooding will raise to about 9% of the projected world-wide Gross Domestic Product, with the U.S., Japan, and the Netherlands remaining the countries with the most publicity. These publicity estimates generally count only on projections of global regular sea stage rise and do not account for vertical land motion.
The analyze calculated the full 1350-kilometer very long coastline of California from 2007-2018, compiling 1000s of satellite visuals in excess of time, used for making a vertical land movement map with 35-million-pixel at ~80 m resolution, comprising a huge selection of coastal uplift and subsidence rates. Coastal communities’ policymakers and the common community can freely down load the facts (link in supplemental information).
The four metropolitan spots majorly afflicted in these spots provided San Francisco, Monterey Bay, Los Angeles, and San Diego.
“The large bulk of the San Francisco Bay perimeter is going through subsidence with rates achieving 5.9 mm/calendar year,” claimed Blackwell. “Notably, the San Francisco International Airport is subsiding with fees more quickly than 2. mm/12 months. The Monterey Bay Spot, like the city of Santa Cruz, is speedily sinking without any zones of uplift. Rates of subsidence for this location access 8.7 mm/12 months. The Los Angeles location shows subsidence together compact coastal zones, but most of the subsidence is developing inland.”
Locations of land uplift bundled north of the San Francisco Bay Area (3 to 5 mm/year) and Central California (identical charge).
Heading forward in the decades ahead, the coastal inhabitants is predicted to mature to more than 1 billion individuals by 2050, due to coastward migration. The potential flood possibility that these communities will confront is primarily managed by the amount of relative sea-level increase, particularly, the mix of sea-degree increase and vertical land motion. It is important to include things like land subsidence into regional projections that are utilised to recognize places of opportunity flooding for the urbanized coast.
Over and above the study, the ASU investigation team is hopeful that some others in the scientific community can develop on their effects to measure and detect coastal dangers more broadly in the U.S. and all around the world.
Reference: “Tracking California’s sinking coast from space: Implications for relative sea-level rise” by Em Blackwell, Manoochehr Shirzaei, Chandrakanta Ojha and Susanna Werth, 31 July 2020, Science Improvements.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba4551



